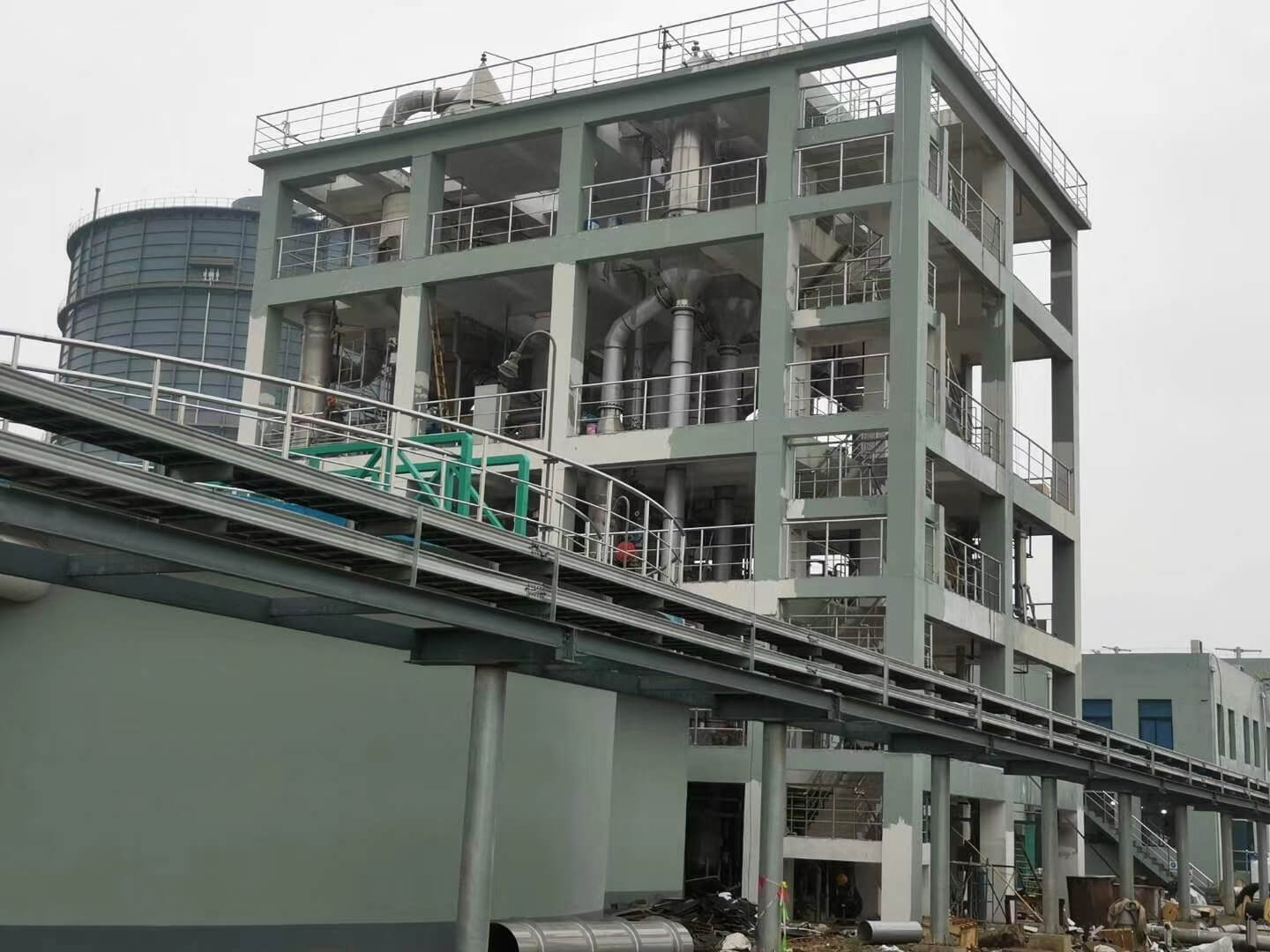
Membrane System
What is Membrane system?
Due to the function of separation, concentration, purification and refining, as well as the features of high efficiency, energy conservation, environmental protection, molecular grade filtration, simple filtration process and it’s easy to control, membrane separation technology has been widely used in many fields, such as food, medicine, biology, environmental, chemical industry, energy, wastewater treatment, electronics, bionics. It has made huge economic and social benefits, becoming one of the most important means in separation science.
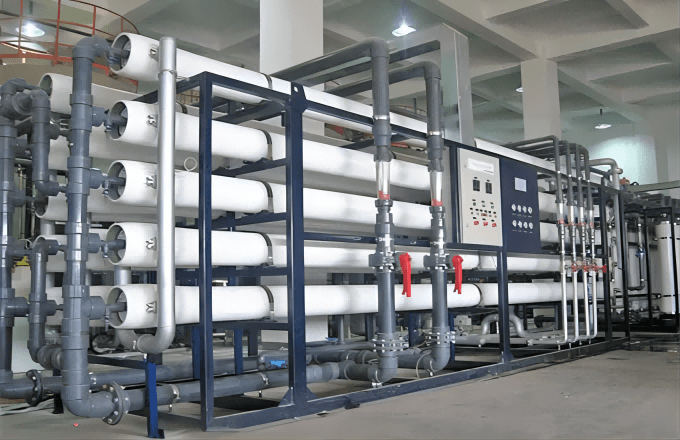
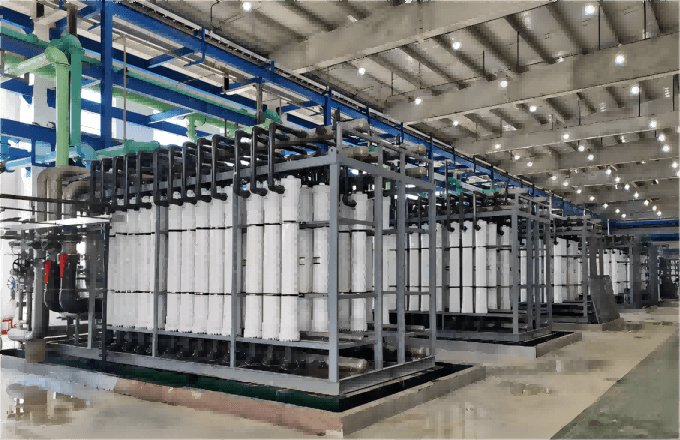


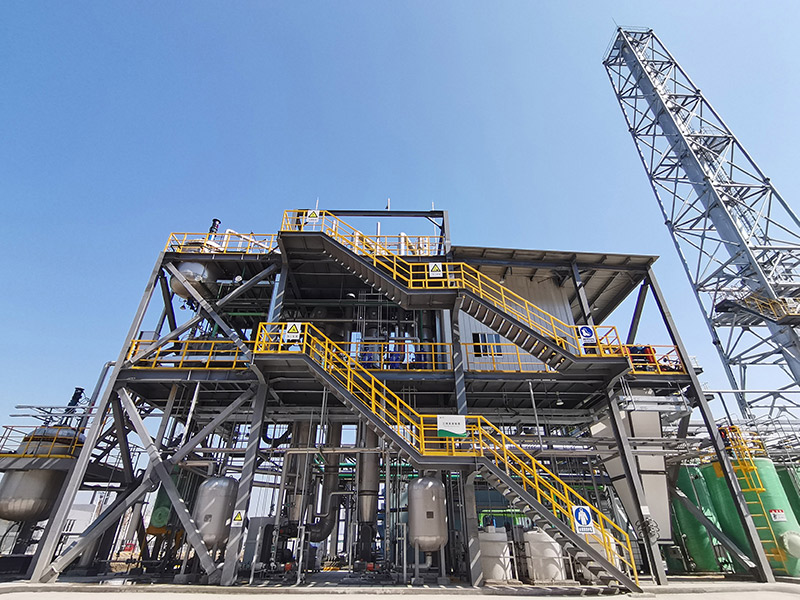
Technologies & Applications
Membrane concentration is a process of concentrating and reducing wastewater by using the selective permeability of the membrane. Nowadays, the commonly used membrane treatment technologies include microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF), reverse osmosis (RO) and membrane distillation technology. It can be roughly divided according to desalting capacity:
microfiltration< ultrafiltration< nanofiltration≤ electrodialysis< reverse osmosis.
- Microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF)
- Reverse osmosis (RO)
- Forward osmosis (FO)
- Electrodialysis
- Membrane distillation
Microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF)
- Microfiltration: With the pressure difference as the driving force, the porous filter membrane as the filtration medium, using the screening principle to separate the insoluble particles (0.1~10 μm), and the operating pressure range is 0.05~0.5Mpa. The microfiltration membrane allows the passage of macromolecules and soluble solids (inorganic salts), but it traps suspended matter, bacteria, and colloids.
- Ultrafiltration: It can intercept 0.001~0.01μm substances, with a formula weight of 1000~300000. It allows the passage of small molecules and soluble solids (inorganic salts), and removes macromolecular organics, colloids, protein, and microorganisms, etc..Ultrafiltration is mainly used in drinking water, industrial wastewater treatment and preparation of high purity water.
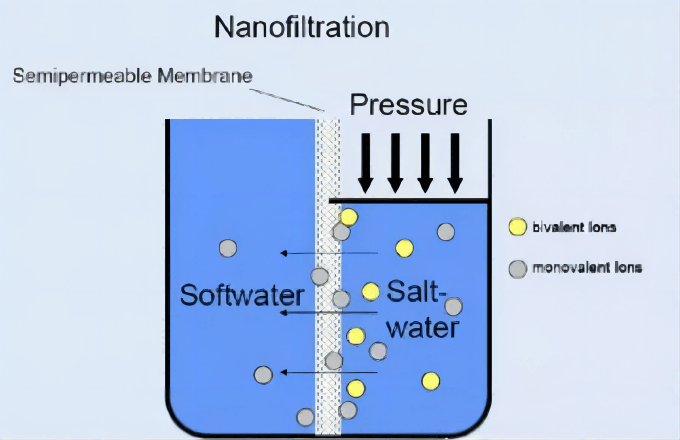
- Nanofiltration: Between reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration, it mainly removes 1nm solute ions, and intercepts the relative molecular mass of 200~1000. The aperture of the nanofiltration membrane is nanoscale, allowing water to pass through, intercepting or partially intercepting substances larger than water molecular weight. The nanofiltration membrane can intercept Ca2+, Mg2+, SO42- and COD, but it allows the passage of Na+ and Cl–.
Reverse osmosis (RO)
- Reverse osmosis is a technology that by providing pressure to the high osmosis pressure side, allowing water molecules to penetrate through the RO membrane to the low osmosis pressure side. With the transfer of water molecules, the concentration of the high-concentration solution is constantly increased. In theory, RO can intercept substances> 0.1nm, and can effectively intercept inorganic salts, colloids and organics with relative molecular weight> 100 in the water. Its desalination rate is as high as 95%~97%, which has the advantages of safety, reliability, stability of discharge water quality.
Reverse osmosis is usually used for water softening, wastewater treatment, the purification, concentration and separation in food, pharmaceutical and chemical industry.
Forward osmosis(FO)
- In contrast to RO technology, forward osmosis is a technology that uses the selective permeability of FO membrane to make water molecules flow through the FO membrane from the lower osmotic pressure side to the higher side. It is a new concentration-driven membrane separation technology that has the advantages of high desalination rate, strong concentration ability, low membrane pollution and high recovery rate. In the concentrated process of wastewater, the absorption liquid with very high concentration must be configured and regenerated to make the water molecules in the wastewater continuously transfer to the absorbing liquid through the FO membrane.
Forward osmosis has been applied in many fields, such as seawater desalination, wastewater treatment, food and drug processing industry. And it becomes a hot topic in membrane separation research in the world.
Background Introduction
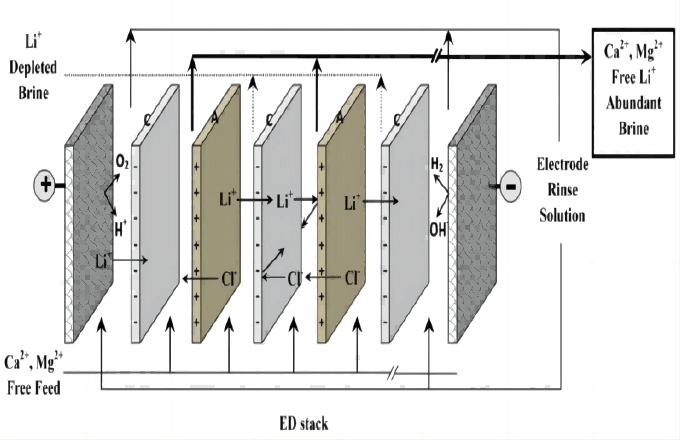
Electrodialysis
- Electrodialysisis is used to transport salt ions from one solution through ion-exchange membranes to another under the influence of an applied electric potential difference. Under the electric field, the ions in the wastewater will move to the opposite electrode driven by the electrode. Because the anion can not pass through the cation membrane and the cation can not pass through the anion membrane, there will be staggered freshwater and the concentrate between the two poles. The concentration effect of electrodialysis is very significant, and the TDS of the concentrate can reach more than 200g/ L, which can greatly reduce the wastewater discharge.
Membrane distillation
- Membrane distillation adopts hydrophobic membrane, which is a membrane separation technology driven by the vapor pressure on both sides of the membrane, suitable for the concentration of non-volatile solute solution.